Building materials are the fundamental substances of construction, determining a building's characteristics, style, and effects. Traditional building materials mainly include stone, wood, clay bricks, lime, and gypsum, while modern building materials encompass steel, cement, concrete, glass, and plastics. Each of them possesses distinctive features and plays a significant role in construction.

Traditional building material
1. Stone
Stone is one of the earliest traditional building materials used in human history. It features abundant reserves, widespread distribution, fine structure, high compressive strength, good water resistance, durability, and excellent wear resistance. Western Europe once widely employed stone in architecture, with notable examples including the magnificent Palace of Versailles in France and the British Parliament House. Additionally, the Egyptian pyramids were constructed using precisely cut large stone blocks. Stone architecture carries an aura of grandeur, solemnity, and nobility. However, due to its high density and weight, stone structures tend to have thicker walls, which reduces the building's floor area ratio. Nevertheless, it can be used as a symbol of luxury in upscale architecture, creating unique artistic effects.
2. Wood
Wood, as a traditional building material, possesses characteristics such as lightweight, high strength, aesthetic appeal, good workability, renewability, recyclability, and being environmentally friendly without pollution. Therefore, wooden structural buildings exhibit excellent stability and seismic resistance. However, wood used in construction also comes with drawbacks. It is prone to deformation, cracking, mold growth, and insect infestation. Moreover, it is susceptible to fire, which can impact its quality and durability.
Wood has been a timeless building material due to its superior mechanical properties and has been widely used in construction activities since ancient times. Certain buildings like parts of Nanchan Temple and Foguang Temple on Mount Wutai in China serve as typical architectural representatives. These structures have gentle, unvarying slopes, extensive eaves, prominent bracketing, and a solemn and simple style.
In modern civil engineering projects, elements such as beams, columns, supports, doors, windows, and even concrete molds rely on wood. As a breathable building material, wood provides warmth in winter and coolness in summer, thus creating the most suitable living environment for humans.
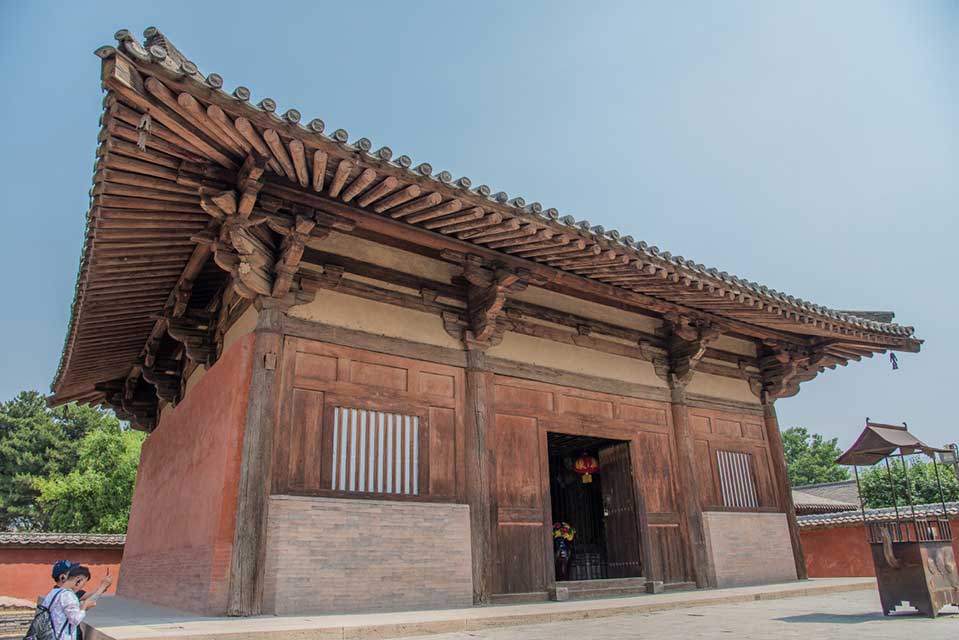

Nanchan Temple, China
3. Clay bricks
Clay bricks are a type of human-made building material. For a long time, common clay bricks have been the main wall material for housing construction in China. Clay bricks are characterized by their small size, light weight, ease of construction, orderly and regular shape, load-bearing capacity, insulation and maintenance capabilities, as well as their facade decoration. Applying them in construction has played a significant role in creating residential spaces for people. The Forbidden City is a typical architectural representation that uses clay bricks. The regular-shaped clay bricks used for the exterior facade contribute to the Forbidden City's impressive artistic effect. However, the raw material for clay bricks is natural clay, and their production involves sacrificing arable land. Gradually, they have been replaced by other materials. Nevertheless, their position in human architectural history will never be erased.
4. Lime
Lime, as a traditional building material, is known for its strong plasticity, slow hardening process, low strength after hardening, and significant volume shrinkage during hardening. Its thousands of years of history testify to humanity's trust and reliance on this material. Lime remains an important building material, widely used in various construction projects and industries, such as interior plastering, mixing lime mortar and grout, and preparing adobe and mud bricks.
Similarly, gypsum, another ancient traditional building material, boasts abundant raw materials, a simple production process, low production energy consumption, strong moisture absorption, affordability, and environmental friendliness. It is particularly suitable for modern architectural interior partitions, decorations, and finishing projects. Additionally, it is primarily used for making gypsum plaster and gypsum products.

Modern building material
5. Steel
Steel plays a crucial role in modern architecture as a building material. Steel possesses excellent qualities such as lightweight yet high strength, good plasticity and toughness, safety and reliability, high industrialization level, fast construction speed, easy dismantling, good sealing properties, and high heat resistance. These premium characteristics make it essential in modern architecture, primarily used in large-span steel structures like airports and stadiums, high-rise building steel structures including hotels and office buildings, towering structures like television and communication towers, plate shell steel structures like large oil storage tanks and gas tanks, industrial factory steel structures, lightweight steel structures like small warehouses, bridge steel structures, and steel structures for moving components like elevators and cranes.
6. Cement
Cement, as a modern building material, finds extensive applications in industrial, agricultural, water resource, transportation, urban development, harbor, and defense construction. In the modern era, it has become an indispensable construction material for any building project. Cement is an inorganic powdered material that, when mixed with water, forms a fluid and malleable paste. Over time, this cement paste undergoes physical and chemical changes, transforming from a malleable paste into a hardened solid with a certain level of strength. It can also bond together solid masses or granular materials to create a unified structure. Cement not only hardens and gains strength when exposed to the air but can also harden in water, maintaining and even improving its strength. Cement is widely used in construction projects, with a broad range of applications in civil engineering, oil and gas infrastructure, dam construction, masonry construction, road construction, and more.
7. Concrete
Concrete, as a modern building material, plays a highly significant role in contemporary construction projects. Concrete is a construction material formed by mixing binding agents such as clay, lime, gypsum, volcanic ash, or natural asphalt with aggregates like sand, slag, and crushed stone. It boasts excellent properties, including strong cohesion, durability, and water resistance. However, concrete is considered a brittle material with high compressive strength but very low tensile strength, making it prone to cracking.
With the introduction of cement and steel, it was discovered that combining these materials provided better bonding strength and allowed them to complement each other's weaknesses while leveraging their strengths. By incorporating steel reinforcement into concrete, it not only protects the steel from exposure to the atmosphere, preventing corrosion but also enhances the structural component's tensile strength. This led to the development of reinforced concrete, expanding the range of applications for concrete in construction.
In comparison to traditional brick and stone structures, wood structures, and steel structures, concrete structures have experienced rapid development and have become the primary structural material in civil engineering. Moreover, high-performance concrete and innovative concrete types continue to advance and evolve in the field of construction.

8. Glass
Furthermore, glass and plastic, as modern innovative building materials, are continuously being employed in contemporary construction projects. Glass can meet the requirements for daylighting, decoration, and facade design, aligning with the energy efficiency demands of modern architecture. Glass finds application in nearly all facets of construction due to its various types, such as tempered glass, semi-tempered glass, insulated glass, laminated glass, tinted glass, coated glass, patterned glass, fire-resistant glass, vacuum glass, and more.

Shanghai-Poly-Grand-Theatre
9. Plastic
Plastic is an emerging class of building material that, due to its excellent performance, wide range of applications, and promising prospects, is considered the fourth major category of construction materials after steel, cement, and wood in modern construction. Plastic has a broad scope of applications, from rooftops to ground surfaces, and from outdoor public facilities to interior decoration materials. Currently, the most common applications of plastic in construction are for water and drainage pipes, gas transmission pipes, and PVC doors and windows, followed by electrical wires and cables.
One of the significant advantages of plastics is their substantial energy-saving potential, with the production and use of plastic products having significantly lower energy consumption compared to other building materials. As a result, plastics are now widely used in various roofing, wall, and flooring construction projects. The field of architectural plastics is continually evolving towards higher functionality, improved performance, versatility, and cost-effectiveness.
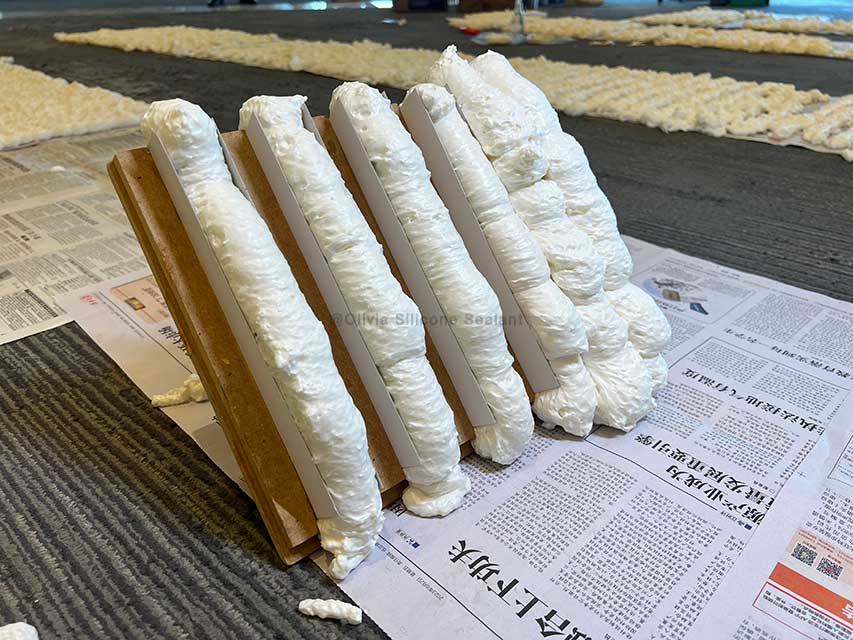
10. Silicone sealant
Silicone sealant is a paste-like substance formed by mixing polydimethylsiloxane as the main raw material with crosslinking agents, fillers, plasticizers, coupling agents, and catalysts under vacuum conditions. At room temperature, it cures and forms elastic silicone rubber through a reaction with moisture in the air. It is used for bonding and sealing various types of glass and other substrates. Currently, Eolya offers multifunctional sealants, including glass sealant, weather-resistant sealant, fire-resistant sealant, stone sealant, metal joint sealant, mold-resistant sealant, decorative joint sealant, and insulated glass sealant, among others, available in multiple types and specifications.
11. Polyurethane foam(PU Foam)
As a new type of building material, polyurethane foam has received widespread attention in recent years. It is synthesized from monomers such as isocyanates and polyols through a polymerization reaction, with the generated carbon dioxide gas serving as a foaming agent. This reaction produces a tightly structured microcellular foam. Polyurethane foam is primarily categorized into rigid polyurethane foam, flexible polyurethane foam, and semi-rigid polyurethane foam. Unlike the closed-cell structure of rigid polyurethane foam, flexible polyurethane foam has an open-cell structure, characterized by its lightweight, breathability, and good resilience. Semi-rigid polyurethane foam is an open-cell type of foam with a hardness between soft and rigid foam, and it has higher compression load values. Rigid polyurethane foam, a novel synthetic material with insulation and waterproofing functions, has a low thermal conductivity and small density, thus often being used as insulation and thermal barrier material in construction.
Compared to traditional construction materials, polyurethane foam possesses outstanding advantages in various aspects, including excellent insulation performance, strong fire resistance, high water resistance, and stable mechanical properties. It can be applied on-site through casting or spraying to form a continuous insulation layer, and has found extensive applications in building exteriors, roofs, floors, doors, windows, and heating pipeline networks.

Compared to traditional and modern building materials, due to advancements in technology and evolving architectural demands, modern building materials offer more advantages than traditional ones. As a result, they have taken a dominant position in contemporary architecture, while traditional building materials are applied in a supplementary role. Modern building materials such as steel, cement, concrete, glass, and composites have broken the constraints of shape and size imposed by traditional materials like stone, wood, clay bricks, and lime gypsum. They have facilitated the development of high-rise, deep-span structures and met the demands of urban construction, aligning with the trends of environmental protection and energy conservation in modern society.
Post time: Aug-31-2023